Contact Dermatitis
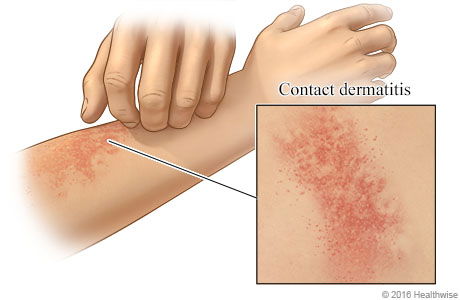
Dermatitis is often acute and refers to an area of irritation usually because of contact with some type of allergen. With acute dermatitis the skin is often darker, thicker and itchier than surrounding unaffected skin.
Chronic dermatitis is also known as Atopic Eczema. This is often characterized by red swollen, scaly, blistering areas. This condition is particularly prevalent in children and usually there is some type of family history of the disease. Psychological stress can provoke or aggravate this condition because it interferes with suppressing normal immune responses.
Seborrheic dermatitis is related to a yeast called pityrosporum ovale (also known as malassezia furfur). People with this form of dermatitis seem to have a reduced resistance to this yeast. For some unknown reason, people with certain neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease and stroke, are particularly prone to this form of dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis appears after puberty. It varies in severity and can persist for years.
Dermatitis is not contagious.
CAUSES OF DERMATITIS
Allergic contact dermatitis is caused by skin contact with substances such as latex, perfume, metals, hair dye and other chemicals that most people do not have a reaction to.
Handling irritants such as detergents and other cleaning solvents, harsh chemicals and friction causes other forms of dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by a reduced resistance to the yeast known as Pityrosporum ovale. It can be aggravated by other illnesses, stress and fatigue. But, compromised general health does not cause it.
DIAGNOSIS
Dermatologists can usually identify the type of dermatitis by sight and when necessary patch testing is performed to determine the source of the allergen.
Treatment
Treatment is available...Come see the Dermatologist for specific treatment.


